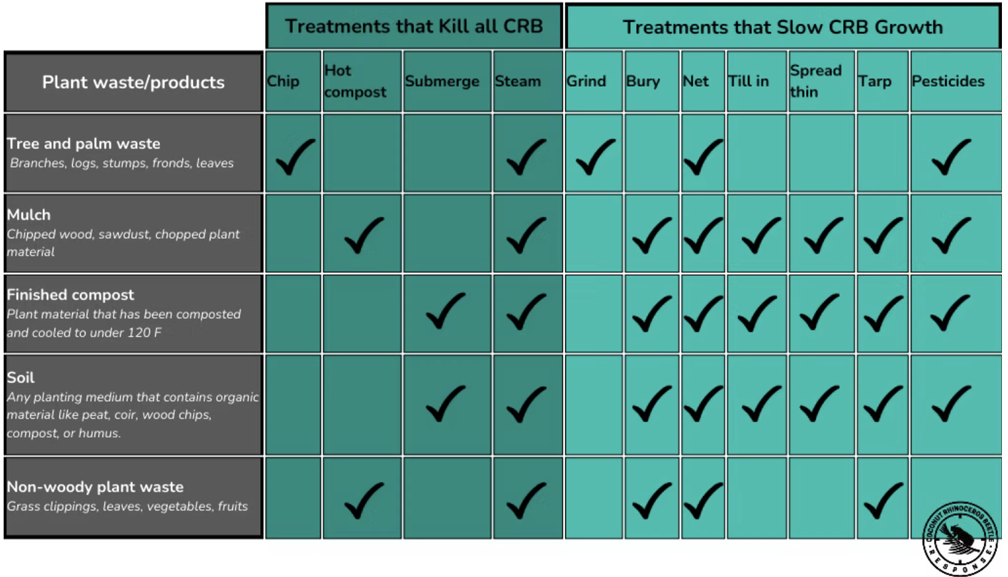
Reduce CRB Breeding Habitat
The key to controlling CRB is reducing their breeding habitat. CRB lay their eggs in any decaying plant matter. We'll call it "green waste" here. It includes compost, mulch, potting mix, stumps, potted plants, dead trees, and piles of organic debris. Below are pictures of some of the most common breeding materials. (courtesy of CRBhawaii.org)
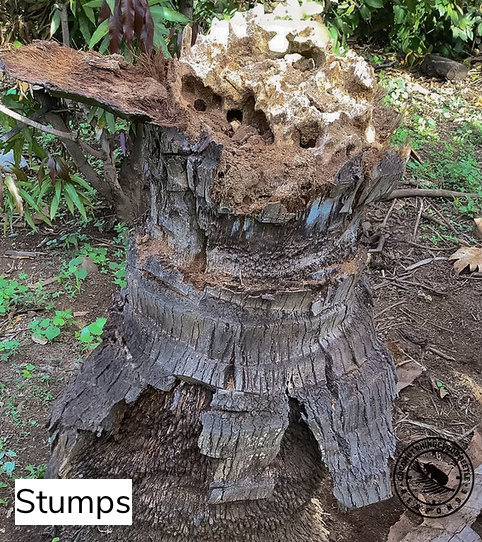
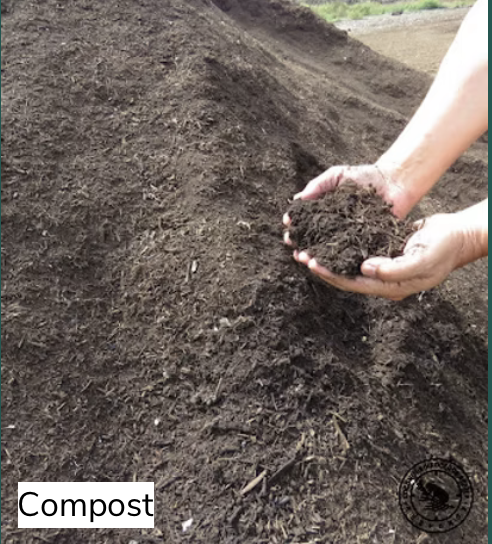








How to Reduce CRB Breeding Material in Lanikai
- Remove It! Lanikai does not have huge masses of CRB breeding material like, for instance, Waimanalo, where mulch is purposely produced in large piles. Removing organic waste is thus our number one strategy. Keep it clean and the CRB will not have good breeding sites.
- Net It! In some cases it might be very difficult to remove a patch of organic debris. Such piles can be netted to prevent CRB from going in, and catch them when they are coming out. Free netting (and guidance) is available for Lanikai residents from the Save Lanikai team.
- Spray it with the the fungus Metarhizium anisopliae (MA for short), a widely used biological insecticide that infects and kills CRB and larvae that it comes into contact with in 3-10 days! Here is a PDF on Biological Insecticides for CRB in Hawaii. This infects CRB where they live most of their lives: in soil and decaying vegetation.